Bitcoin mining has gained significant attention in recent years, not only for its role in powering the Bitcoin network but also for its environmental impact. As the cryptocurrency market continues to grow, so does the concern regarding the ecological consequences of mining activities. In this article, we will delve into the Bitcoin mining environmental impact, discussing both current and future challenges, and exploring potential solutions for sustainable practices.
1. Understanding Bitcoin Mining
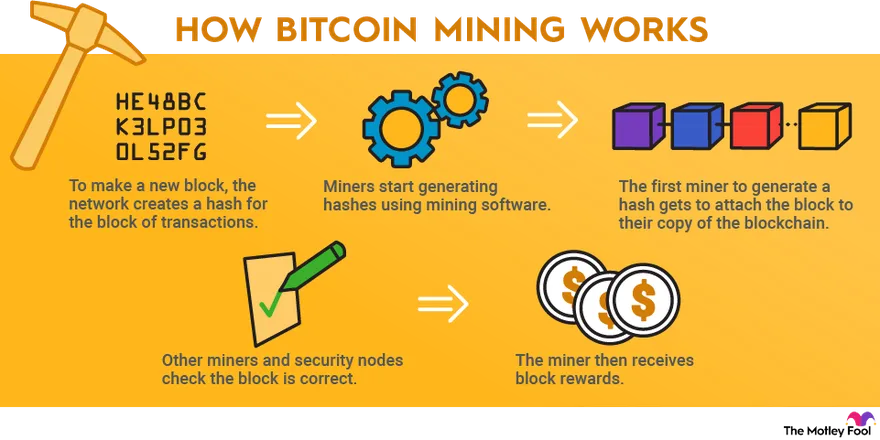
Before we explore the Bitcoin mining environmental impact, it’s essential to understand what Bitcoin mining entails. Bitcoin mining is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the public ledger known as the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and in return, they are rewarded with newly created bitcoins.
1.1 How Bitcoin Mining Works
Bitcoin mining relies on a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW). This system requires miners to compete against each other to solve cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with bitcoins. This process requires significant computational power, which translates into high energy consumption.
1.2 The Growth of Bitcoin Mining
As Bitcoin’s popularity has surged, so has the number of miners. According to the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, Bitcoin’s energy consumption has grown exponentially, raising questions about its sustainability. The Bitcoin mining environmental impact is increasingly scrutinized as miners seek more efficient methods to maintain profitability.
2. The Environmental Challenges of Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin mining environmental impact primarily stems from its energy consumption and carbon footprint. Here are five critical challenges facing the industry:
2.1 High Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining is notorious for its high energy consumption. Estimates suggest that the Bitcoin network consumes more energy annually than some countries. This excessive energy use can strain local power grids and contribute to increased greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Sources: The environmental impact varies significantly depending on the energy sources used. Regions that rely on fossil fuels, such as coal, contribute disproportionately to the carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining.
2.2 Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining is a pressing concern. Studies indicate that Bitcoin mining generates a substantial amount of carbon dioxide emissions. For instance, if miners predominantly use coal-powered energy, the environmental impact is significantly heightened.
- Comparison with Traditional Banking: Some proponents argue that Bitcoin’s energy consumption should be compared to that of the traditional banking system. However, the lack of transparency in energy sources used for mining makes this comparison complex.
2.3 E-Waste Generation
The hardware used for Bitcoin mining has a limited lifespan, leading to significant electronic waste (e-waste) generation. Specialized mining equipment, such as ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners, becomes obsolete quickly as technology advances.
- E-Waste Management: Improper disposal of e-waste can harm the environment, releasing toxic substances into the soil and water. The Bitcoin mining environmental impact includes not only energy consumption but also the management of e-waste.
2.4 Water Usage
In addition to energy consumption, Bitcoin mining operations often require substantial amounts of water for cooling purposes. Data centers that host mining equipment need to maintain optimal temperatures to prevent overheating.
- Regional Concerns: In water-scarce regions, this demand can exacerbate existing water shortages, raising ethical concerns about resource allocation.
2.5 Regulatory Challenges
As awareness of the Bitcoin mining environmental impact grows, governments and regulatory bodies are starting to take action. Stricter regulations on energy use and emissions could pose challenges for miners, particularly in regions where mining is concentrated.
- Future Regulations: Future regulations may lead to increased costs for miners, forcing them to adopt more sustainable practices or potentially shutting down operations that do not comply.
3. Exploring Solutions for Sustainable Bitcoin Mining
To mitigate the Bitcoin mining environmental impact, industry stakeholders must consider various strategies:
3.1 Transition to Renewable Energy
One of the most effective ways to reduce the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining is by transitioning to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can significantly lower the carbon footprint associated with mining operations.
- Examples of Renewable Mining Operations: Several mining companies have already begun using renewable energy sources. For instance, some miners are establishing operations near hydroelectric plants to take advantage of low-cost, clean energy.
3.2 Energy Efficiency Improvements
Improving energy efficiency in mining operations can also help reduce the environmental impact. Miners can invest in advanced hardware that consumes less power while delivering higher performance.
- Optimizing Mining Operations: Techniques such as load balancing and optimizing cooling systems can further enhance energy efficiency.
3.3 Implementing E-Waste Recycling Programs
To address the issue of e-waste, the Bitcoin mining industry should implement recycling programs for outdated mining equipment. By properly recycling electronic components, miners can reduce their overall environmental impact.
- Collaborating with E-Waste Recyclers: Partnerships with certified e-waste recycling facilities can ensure responsible disposal and recovery of valuable materials.
3.4 Community Engagement and Transparency
Fostering a culture of transparency and community engagement can help address concerns about the Bitcoin mining environmental impact. Miners should communicate their energy sources and sustainability practices to build trust with the public.
- Public Relations Efforts: Engaging with local communities and stakeholders can help mitigate negative perceptions and foster collaboration on sustainability initiatives.
3.5 Exploring Alternative Consensus Mechanisms
While transitioning to renewable energy and improving efficiency are essential steps, the Bitcoin network may also consider exploring alternative consensus mechanisms. Some cryptocurrencies have adopted Proof of Stake (PoS) or other less energy-intensive models to reduce environmental impacts.
- The Future of Bitcoin’s Consensus Model: Although Bitcoin is unlikely to switch from PoW in the near future, discussions around this topic could influence the broader cryptocurrency landscape.
4. The Future of Bitcoin Mining and Its Environmental Impact
As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, so will the Bitcoin mining environmental impact. Industry stakeholders must remain proactive in addressing the challenges and finding sustainable solutions.
4.1 Innovations in Mining Technology
Emerging technologies can revolutionize the mining landscape. Innovations such as liquid cooling systems, more efficient mining hardware, and energy recovery systems can significantly reduce the environmental impact.
- The Role of Research and Development: Investment in research and development will be critical to driving these innovations forward.
4.2 Increased Regulatory Scrutiny
As governments become more aware of the Bitcoin mining environmental impact, increased regulatory scrutiny is likely. This may include stricter emissions targets, energy consumption limits, and requirements for transparency regarding energy sources.
- Adapting to New Regulations: Miners will need to adapt to these changes by adopting sustainable practices and reporting their energy usage accurately.
4.3 Collaboration Across the Industry
Collaboration among miners, energy providers, and regulators will be essential for finding solutions to the Bitcoin mining environmental impact. By working together, stakeholders can develop best practices and standards that promote sustainability.
- Industry Initiatives: Several industry initiatives are already underway, focusing on reducing energy consumption and promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin mining environmental impact poses significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure the sustainability of the industry. By understanding the current issues and exploring solutions, stakeholders can work together to create a more environmentally responsible future for Bitcoin mining. As we move forward, the commitment to innovation, efficiency, and sustainability will be crucial in mitigating the negative effects of this burgeoning industry.